Leveraging Men’s Education as an Effective Pathway for Improving Diet Quality: Evidence from Rural India
Abstract
Read a policy brief based on this study.
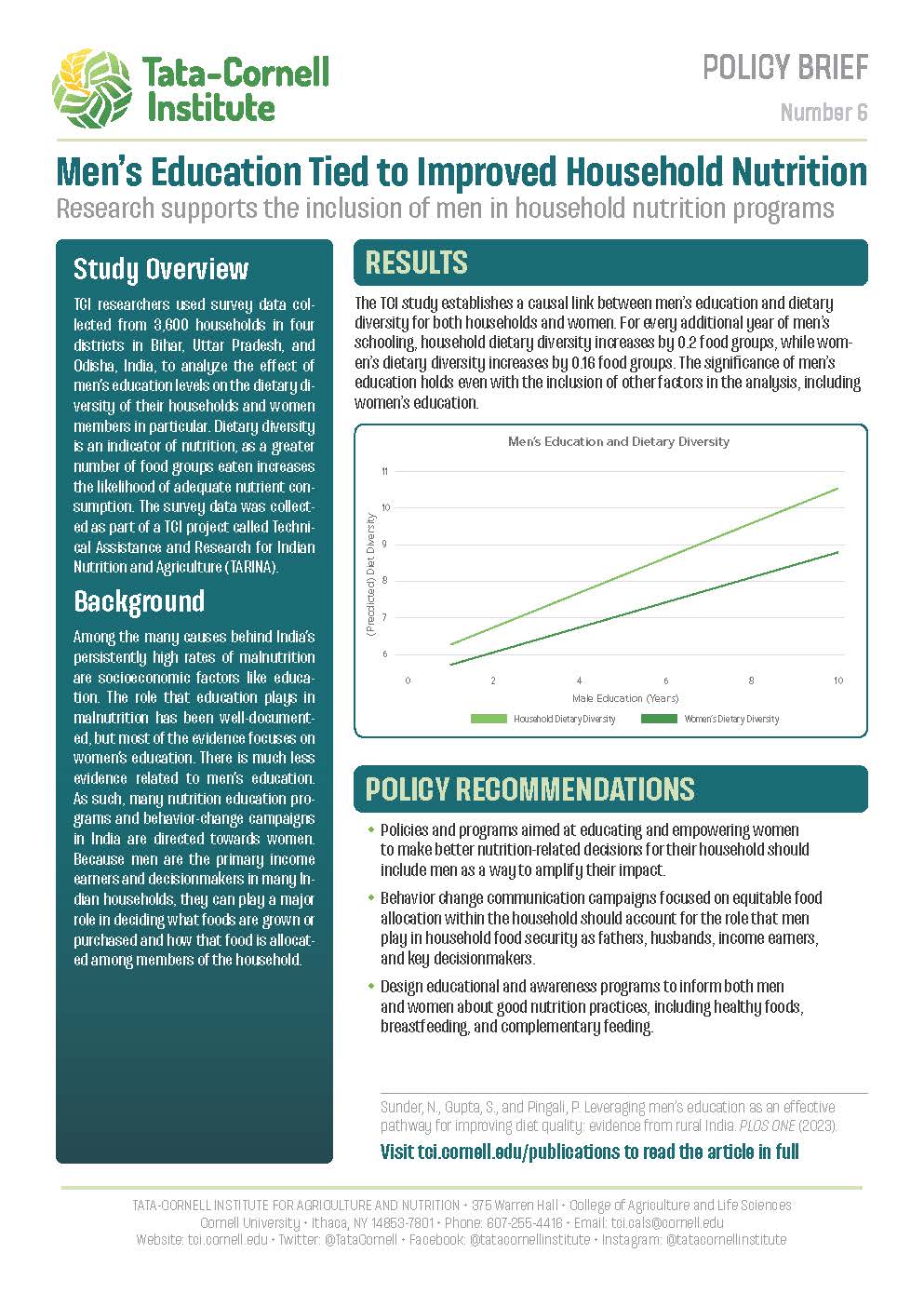
Investing in nutrition-sensitive sectors such as education can be an effective strategy for combatting malnutrition. In this paper, we analyze the role that men’s education plays in determining dietary diversity outcomes using primary data from 3600 households across four districts of India. Dietary diversity scores were calculated to reflect the quality of food intake, for households and women. Men’s education level was considered as the primary driver of diet diversity. To establish a causal link between men’s education and diet diversity, the education levels of parents and siblings were used as instrumental variables. We find that men’s education levels are associated with significantly higher diet diversity scores both for the household and for women. The role of men’s education continues to be a significant determinant of diet quality after controlling for household and individual-level confounding factors including the education level of the woman. The results are consistent across different definitions of the diet diversity score and reference period. Methodologically we extend the evidence on the education–nutrition pathway from being associational to causal in nature. Results from this study point to the benefits of leveraging men’s education as an effective pathway for improving nutritional outcomes within households.

